It has not been long before the whole world has gone thru the scare that was known as the NIPA virus. Now, it seems another even deadlier threat has arrived and this post is about what precautions we can take to prevent being affected.

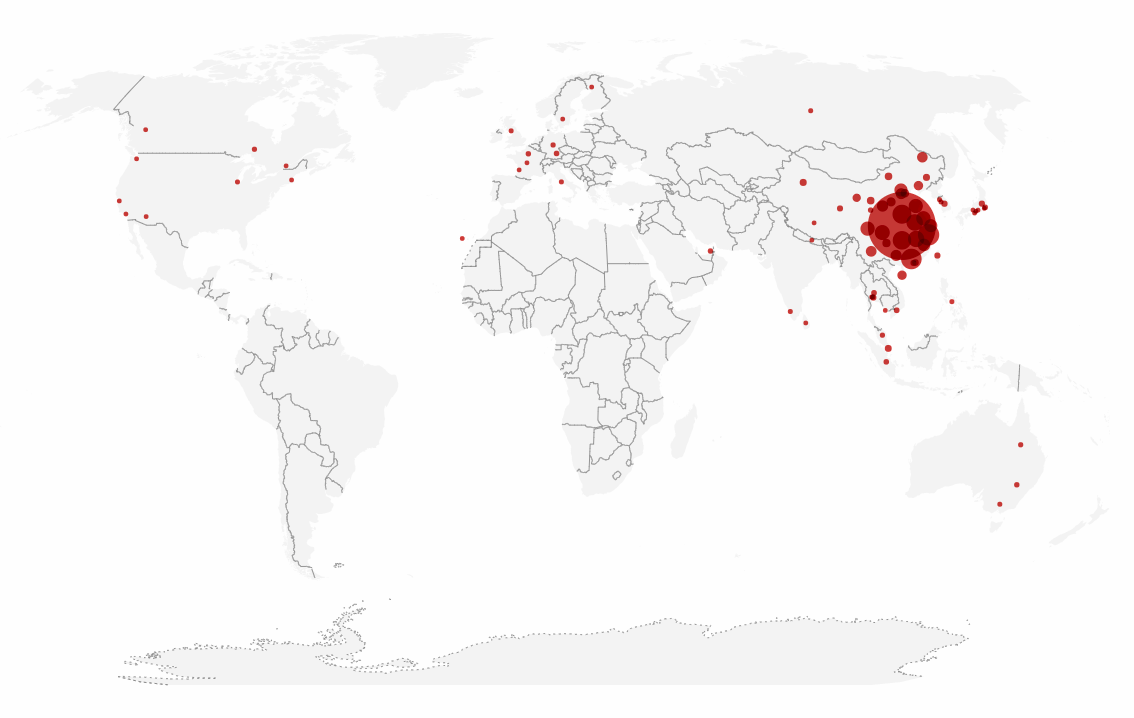
2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) is a virus (more specifically, a coronavirus) identified as the cause of an outbreak of respiratory illness first detected in Wuhan, China. Early on, many of the patients in the outbreak in Wuhan, China reportedly had some link to a large seafood and animal market, suggesting animal-to-person spread. However, a growing number of patients reportedly have not had exposure to animal markets, indicating person-to-person spread is occurring. At this time, it’s unclear how easily or sustainably this virus is spreading between people.
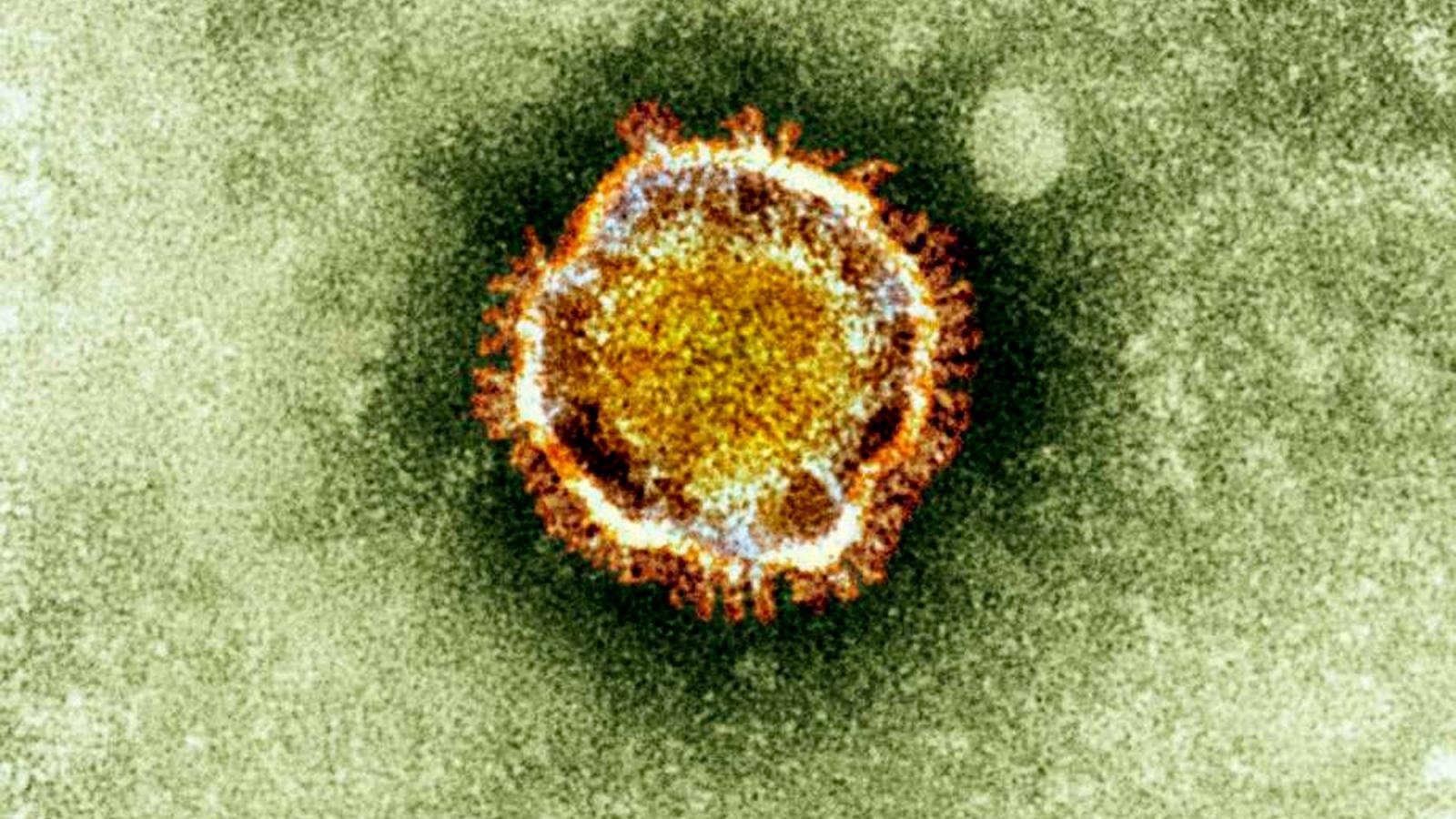
Transmission
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are common in many different species of animals, including camels, cattle, cats, and bats. Rarely, animal coronaviruses can infect people and then spread between people such as with MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) and SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome). When person-to-person spread has occurred with MERS and SARS, it is thought to have happened mainly via respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes, similar to how influenza and other respiratory pathogens spread. Spread of SARS and MERS between people has generally occurred between close contacts.

It’s important to note that how easily a virus spreads person-to-person can vary. Some viruses are highly contagious (like measles), while other viruses are less so. It’s important to know this in order to better understand the risk associated with this virus. Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are common in many different species of animals, including camels, cattle, cats, and bats. Rarely, animal coronaviruses can infect people and then spread between people such as with MERS and SARS. When person-to-person spread has occurred with MERS and SARS, it is thought to have happened mainly via respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes, similar to how influenza and other respiratory pathogens spread. Spread of SARS and MERS between people has generally occurred between close contacts.
It’s important to note that how easily a virus spreads person-to-person can vary. Some viruses are highly contagious (like measles), while other viruses are less so. It’s important to know this in order to better understand the risk associated with this virus. For confirmed 2019-nCoV infections, reported illnesses have ranged from people being mildly sick to people being severely ill and dying. Symptoms can include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of Breath
At this time the symptoms of 2019-nCoV may appear in as few as 2 days or as long as 14 after exposure. This is based on what has been seen previously as the incubation period of MERS viruses.
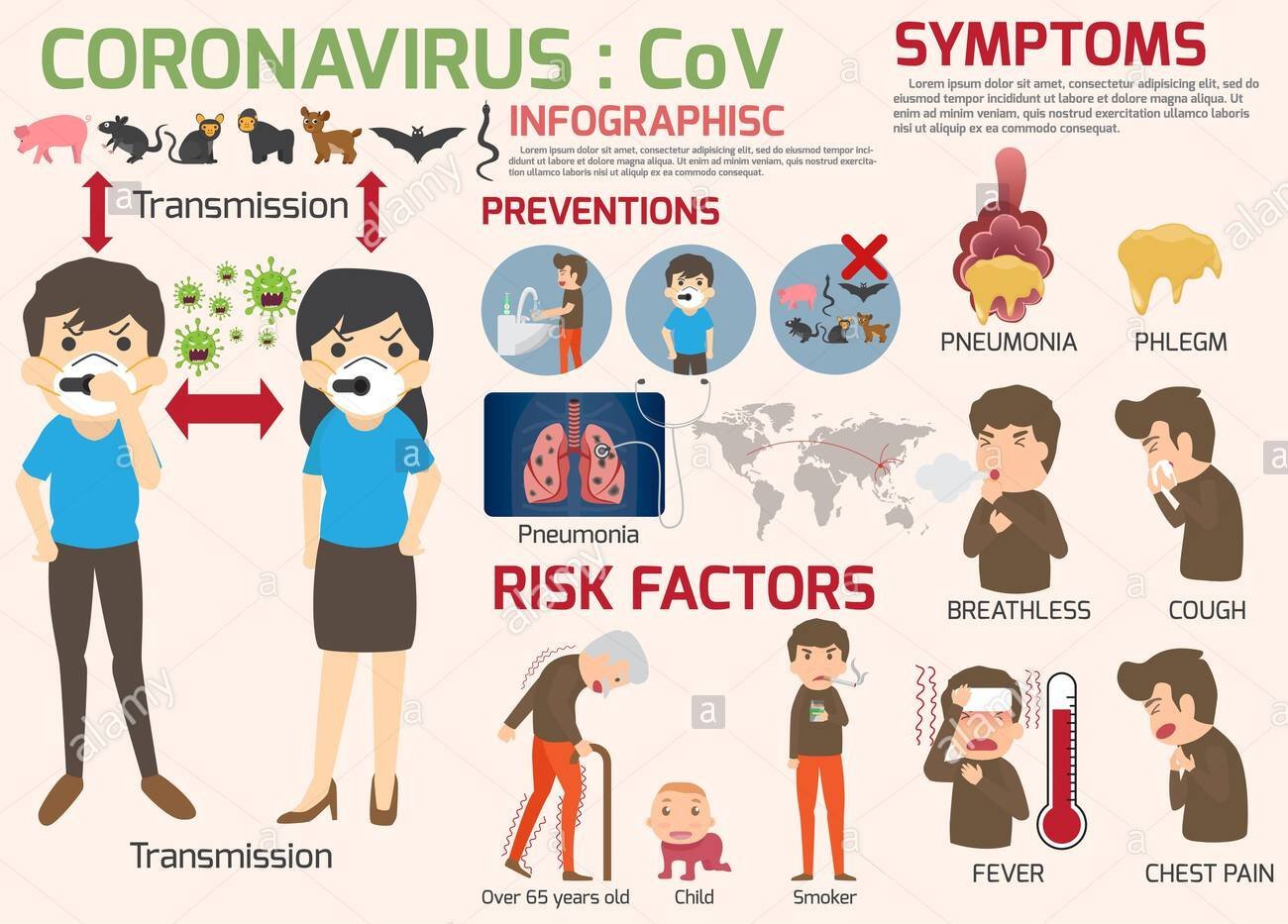
Prevention
There is currently no vaccine to prevent 2019-nCoV infection. The best way to prevent infection is to avoid being exposed to this virus.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Use an alcohol-based hand sanitiser that contains at least 60% alcohol if soap and water are not available.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands.
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- Stay home when you are sick.
- Cover your cough or sneeze with a tissue, then throw the tissue in the trash.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces.
Treatment
There is no specific antiviral treatment recommended for 2019-nCoV infection. People infected with 2019-nCoV should receive supportive care to help relieve symptoms. For severe cases, treatment should include care to support vital organ functions.
People who think they may have been exposed to 2019-nCoV should contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Recently Returned Travellers From China
If you were in China in the last 14 days and feel sick with fever, cough, or difficulty breathing, you should:
- Seek medical care right away. Before you go to a doctor’s office or emergency room, call ahead and tell them about your recent travel and your symptoms.
- Avoid contact with others.
- Not travel while sick.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Wash hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds to avoid spreading the virus to others.
- Use an alcohol-based hand sanitiser that contains at least 60% alcohol if soap and water are not available.
If You Travelled To China And Now You Are Back
All travellers from China, including business travellers, people who visited friends and family, and humanitarian workers should take the following steps.
- First, watch for any changes in your health for 14 days after leaving China. If you get a fever or develop a cough or difficulty breathing during this 14-day period, avoid contact with others.
- Call your doctor or healthcare provider to tell them about your symptoms and your recent travel. They will provide further instruction about steps to take before your medical visit to help to reduce the risk that you will spread your illness to other people in the office or waiting room, if that is what has made you sick.
- Don’t travel while you are sick.

Official Information From CDC
Please do check these out:



The Writer is a Medical Student.